
A unified model of codon reassignment in alternative genetic codes. Transfer RNA mutation and the malleability of the genetic code. Codon reassignment (codon capture) in evolution. A new noncanonical nuclear genetic code: translation of UAA into glutamate. Sanchez-Silva, R., Villalobo, E., Morin, L.
Trna codons code#
The molecular basis of nuclear genetic code change in ciliates. Obligately phagotrophic aphelids turned out to branch with the earliest-diverging fungi. Characterisation of a non-canonical genetic code in the oxymonad Streblomastix strix. Augmented genetic decoding: global, local and temporal alterations of decoding processes and codon meaning. A computational screen for alternative genetic codes in over 250,000 genomes. Position-dependent termination and widespread obligatory frameshifting in Euplotes translation. Origin and evolution of the genetic code: the universal enigma. The coevolution of genes and genetic codes: Crick’s frozen accident revisited. Novel ciliate genetic code variants including the reassignment of all three stop codons to sense codons in Condylostoma magnum. Genetic codes with no dedicated stop codon: context-dependent translation termination. A precedented nuclear genetic code with all three termination codons reassigned as sense codons in the syndinean Amoebophrya sp. An unprecedented non-canonical nuclear genetic code with all three termination codons reassigned as sense codons. Hence, we describe a previously unknown, universal mechanism that has been exploited in unrelated eukaryotes with reassigned stop codons. Virtually the same strategy has been adopted by the ciliate Condylostoma magnum. nonstop release factor 1 acquired a mutation that specifically restricts UGA recognition, robustly potentiating the UGA reassignment. nonstop, Trypanosoma brucei and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and expressing them in the last two species, we recorded a significantly higher readthrough for all 4-bp variants. Mimicking this evolutionary twist by engineering both variants from B. The canonical 5-bp tRNA Trp recognizes UGG as dictated by the genetic code, whereas its shortened 4-bp variant incorporates tryptophan also into in-frame UGA.
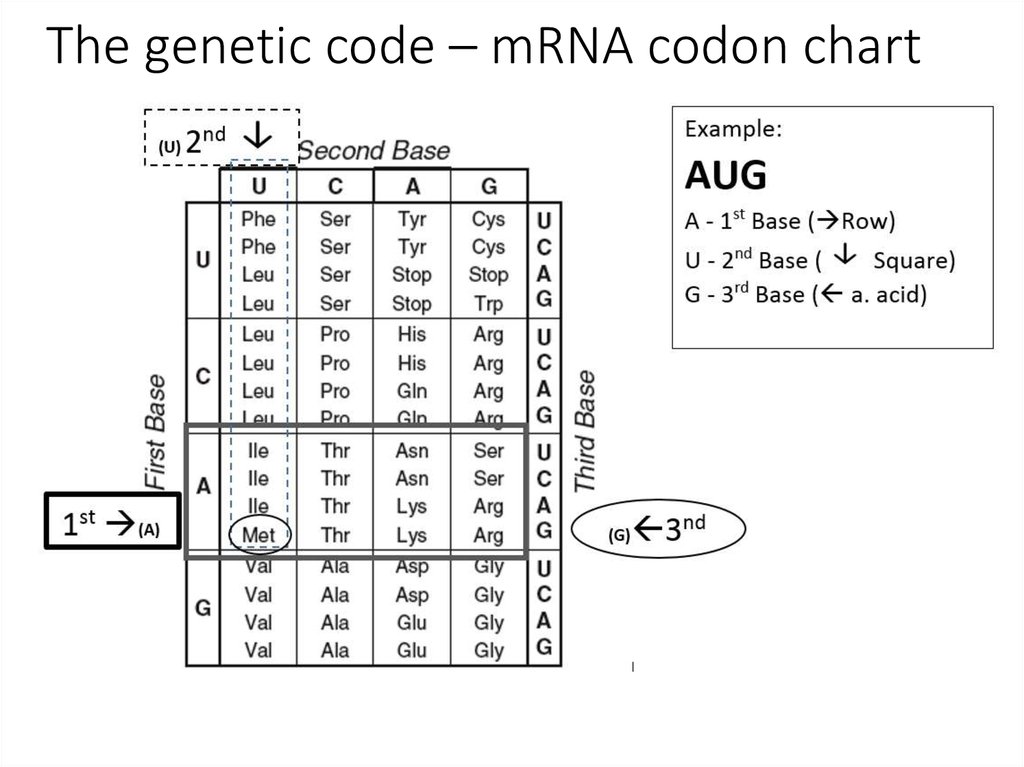
Whereas new tRNAs Glu fully cognate to UAG and UAA evolved to reassign these stop codons, the UGA reassignment followed a different path through shortening the anticodon stem of tRNA Trp CCA from five to four base pairs (bp). We reveal that in this species in-frame stop codons are underrepresented in genes expressed at high levels and that UAA serves as the only termination codon. Here we analyse the in-frame stop codons in 7,259 predicted protein-coding genes of a previously undescribed trypanosomatid, Blastocrithidia nonstop. Some protists have reassigned all stop codons as sense codons, neglecting this fundamental principle 1, 2, 3, 4. Cognate tRNAs deliver specific amino acids to translating ribosomes according to the standard genetic code, and three codons with no cognate tRNAs serve as stop codons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
